Prediction of water inrush from coal seam floor based on machine learning with small sample data
-
摘要:
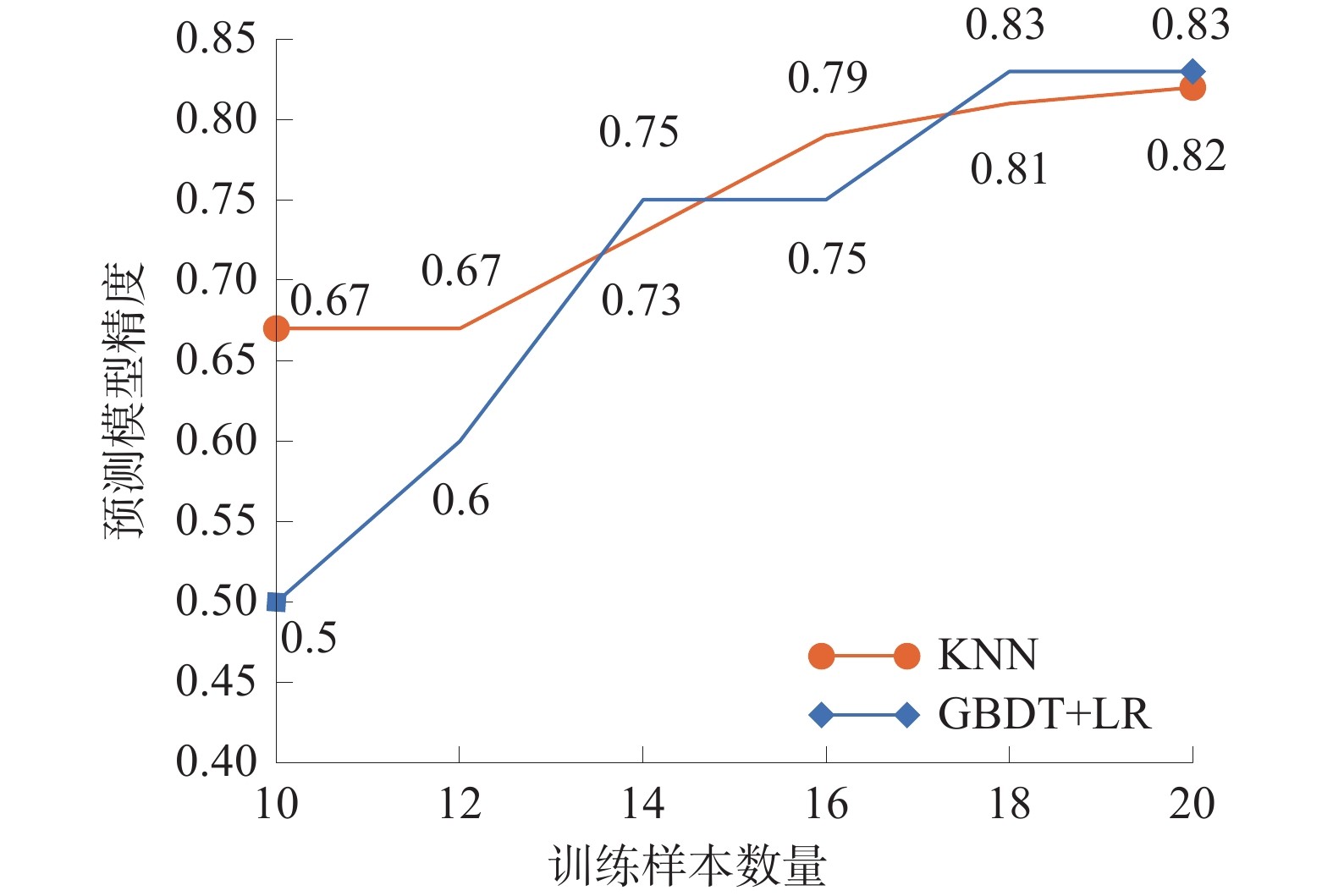
随着计算机技术的发展,机器学习方法已成为煤层底板突水预测的重要技术;算法预测精准度对样本的数量要求较高,制约着实际应用。运用最近邻算法(KNN)以及梯度提升决策树(GBDT)与逻辑回归(LR)结合运用的算法,基于以水压、采高、隔水层厚度、断层落差、煤层倾角、断层距工作面距离等6项指标的样本数据建立了突水预测模型,讨论了样本数量对预测精度的影响规律,并与常用的粒子群、支持向量机、BP神经网络、随机森林以及卷积神经网络进行对比研究。研究结果表明:当样本数量达到18时,KNN和GBDT+LR预测精度保持稳定;KNN与GBDT+LR在小样本条件下的预测精度高于常规预测模型;模型预测结果与实际情况相符。
Abstract:With the development of computer technology, machine learning method has become an important technology for the prediction of water inrush in coal seam floor. However, the prediction accuracy of many machine learning algorithms requires a high number of samples, which restricts the practical application. In this paper, by using the nearest neighbor algorithm (KNN) and the combination algorithm of gradient boosting decision tree (GBDT) and logistic regression (LR), a water inrush prediction model was established based on the sample data of six indexes, including water pressure, mining height, water-barrier thickness, fault drop, coal seam inclination, and fault distance from the working face. The influence rule of sample number on prediction accuracy was discussed, and the comparison study was conducted with the commonly used particle swarm, support vector machine, BP neural network, random forest and convolutional neural network. The results show that when the number of samples reaches 18, the prediction accuracy of KNN and GBDT+LR remains stable. The prediction accuracy of KNN and GBDT+LR is higher than that of conventional models under small sample conditions. The predicted results of the model agree with the actual situation.
-
表 1 训练数据
Table 1 Training data
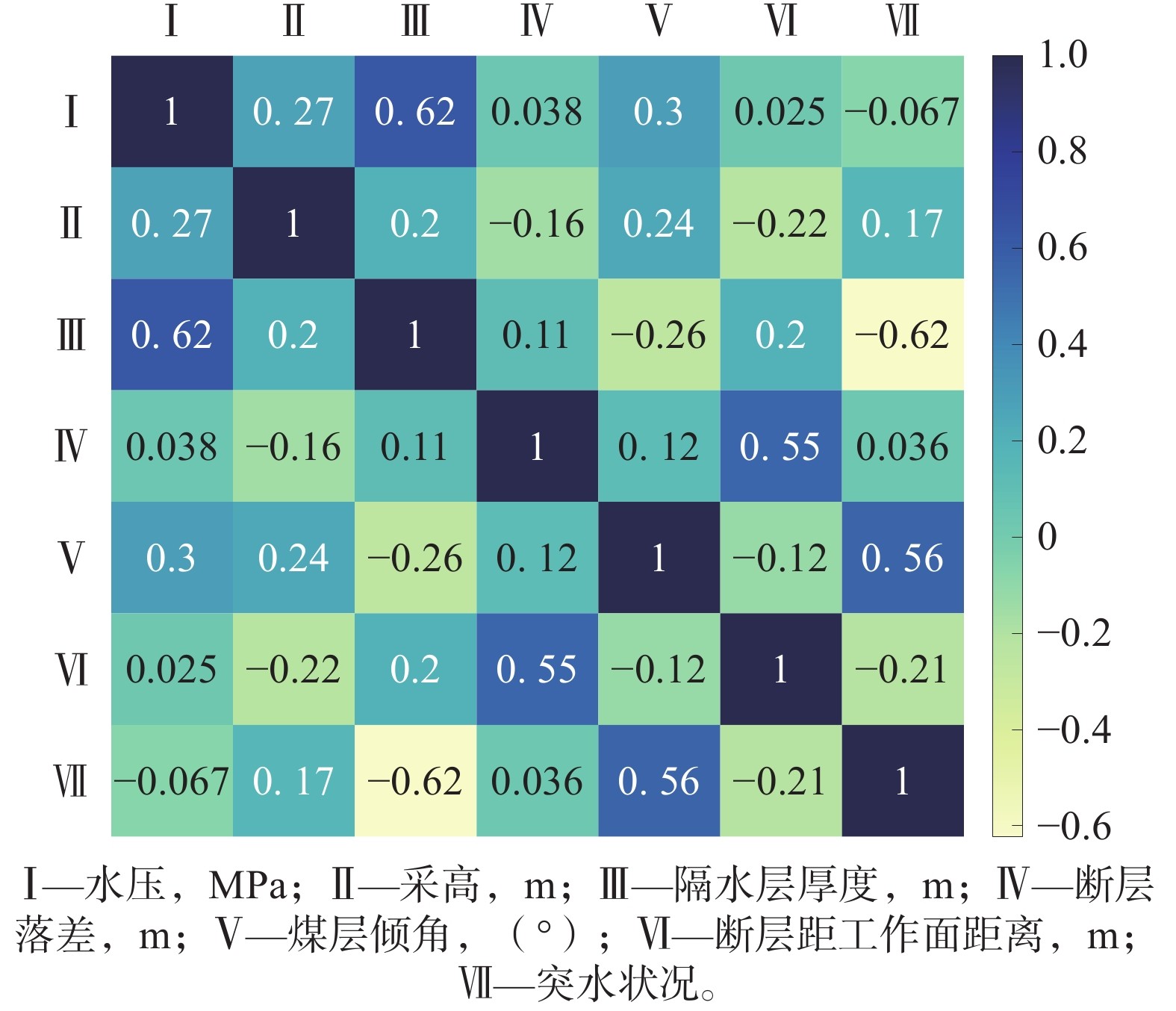
名称 水压/MPa 采高/m 隔水层厚度/m 断层落差/m 煤层倾角/(º) 断层距工作面距离/m 突水状况 夏庄煤矿 1.82 0.80 26.39 4.00 12 16 是 夏庄煤矿 1.65 1.60 25.85 50.00 17 90 是 夏庄煤矿 1.00 0.90 22.33 2.00 13 16 是 夏庄煤矿 2.88 1.00 17.68 1.30 20 0 是 井陉三煤矿 2.01 8.00 28.00 0.60 18 10 是 井陉三煤矿 1.91 8.00 43.00 1.50 11 2 是 洪山煤矿 1.33 0.85 36.38 0.80 7 62 否 洪山煤矿 0.95 1.45 26.89 1.00 6 55 否 洪山煤矿 0.92 1.40 33.61 0.50 8 0 否 洪山煤矿 0.34 0.90 32.65 22.00 6 6 否 黑山煤矿 1.06 2.00 27.79 0.46 7 21 否 黑山煤矿 0.83 2.85 26.56 0.70 12 6 否 谢一矿33采区底板 2.00 2.81 30.00 1.50 18 12 是 九里山煤矿12031工作面 1.80 1.90 23.00 0 15 17 是 潘东井106工作面 1.70 2.80 10.00 5.00 17 10 是 肥城陶阳煤矿9901工作面 0.60 1.10 17.00 8.00 19 6 是 华泰351504工作面 2.10 1.60 59.50 3.50 10 39 否 潘西6197工作面 2.80 2.75 69.17 11.70 12 36 否 潘西6196工作面 2.80 2.55 66.11 16.00 12 29 否 新汶协庄煤矿31104工作面 1.30 1.70 30.00 4.90 5 21 是 表 2 测试数据
Table 2 Test data
名称 水压/MPa 采高/m 隔水层厚度/m 断层落差/m 煤层倾角/(º) 断层距工作面距离/m 突水状况 华泰31503 1.08 0.90 16.50 3.2 7 7 是 良庄51302 1.10 1.60 20.00 15.0 11 16 是 潘西6194 4.06 2.75 65.86 10.0 10 11 否 白庄9602 3.11 2.61 44.30 3.5 11 12 是 华恒61106 2.70 2.55 66.97 16.0 12 31 否 表 3 测试结果
Table 3 Test results
名称 SVM PSO_SVM BPnet RF CNN KNN GBDT+LR 实际情况 华泰31503 未突水 未突水 突水 未突水 未突水 突水 突水 突水 良庄51302 突水 突水 突水 突水 未突水 突水 突水 突水 潘西6194 未突水 未突水 突水 未突水 未突水 未突水 未突水 未突水 白庄9602 未突水 突水 突水 未突水 未突水 突水 突水 突水 华恒61106 未突水 未突水 未突水 未突水 未突水 未突水 未突水 未突水 正确率 0.6 0.8 0.8 0.6 0.4 1 1 1 -
[1] 施龙青,谭希鹏,王娟,等. 基于PCA_Fuzzy_PSO_SVC的底板突水危险性评价[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(1):167−171. SHI Longqing, TAN Xipeng, WANG Juan, et al. Risk assessment of water inrush based on PCA_Fuzzy_PSO_SVC[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(1): 167−171.
[2] WU Q, WANG M, WU X. Investigations of groundwater bursting into coal mine seam floors from fault zones[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2004, 41(4): 557−571. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2003.01.004
[3] 李忠建,魏久传,郭建斌,等. 运用突水系数法和模糊聚类法综合评价煤层底板突水危险性[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2010,37(1):24−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2010.01.009 LI Zhongjian, WEI Jiuchuan, GUO Jianbin, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of water-inrush risk from coal floor by both water-inrush coefficientand fuzzy cluster methods[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2010, 37(1): 24−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2010.01.009
[4] 李飞,孔德中,汪洋,等. 我国煤层底板突水机理与防治研究现状及展望[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(11):200−206. LI Fei, KONG Dezhong, WANG Yang, et al. Research status and prospect of water inrush mechanism and prevention of coal seam floor in China[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(11): 200−206.
[5] 王进尚,姚多喜,黄浩. 煤矿隐伏断层递进导升突水的临界判据及物理模拟研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(7):2014−2020. WANG Jinshang, YAO Duoxi, HUANG Hao. Critical criterion and physical simulation research on progressive ascending water inrush in hidden faults of coal mines[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(7): 2014−2020.
[6] ZHANG J C. Investigations of water inrushes from aquifers under coal seams[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2005, 42(3): 350−360. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.11.010
[7] 李白英. 预防矿井底板突水的“下三带”理论及其发展与应用[J]. 山东矿业学院学报(自然科学版),1999(4):11−18. LI Baiying. “Down Three Zones” in the prediction of the water inrush from coalbed floor aquifer theory, development and application[J]. Journal of Shandong Mining Institute(Natural Science Edition), 1999(4): 11−18.
[8] 李万军,杨家兵. “下三带”理论和“P-h”临界曲线法预测底板突水[J]. 煤矿开采,2010,15(5):45−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6225.2010.05.016 LI Wanjun, YANG Jiabing. “Down 3 zones” theory and “P-h” critical curve method for floor water-bursting forecast[J]. Coal Mining Technologg Technology, 2010, 15(5): 45−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6225.2010.05.016
[9] 钱鸣高,缪协兴,许家林. 岩层控制的关键层理论[M]. 徐州:中国矿业大学出版社,2000. [10] 周永章,王俊,左仁广,等. 地质领域机器学习、深度学习及实现语言[J]. 岩石学报,2018,34(11):3173−3178. ZHOU Yongzhang, WANG Jun, ZUO Renguang, et al. Machine learning, deep learning and Python language in field of geology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 34(11): 3173−3178.
[11] 温廷新,孙雪,田洪斌,等. 基于PCA_Fuzzy_RF模型的煤层底板突水预测[J]. 安全与环境学报,2017,17(3):855−858. WEN Tingxin, SUN Xue, TIAN Hongbin, et al. Prediction of the water inrush from the coal seam based on PCA_Fuzzy_ RF model[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2017, 17(3): 855−858.
[12] 陈建平,王春雷,王雪冬. 基于CNN神经网络的煤层底板突水预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(1):50−57. CHEN Jianping, WANG Chunlei, WANG Xuedong. Coal mine floor water inrush prediction based on CNN neural network[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(1): 50−57.
[13] 陈桂军,张雪英,李凤莲,等. 基于εN-SVDD算法的煤层底板突水危险性预测[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版),2018,37(1):21−26. doi: 10.11956/j.issn.1008-0562.2018.01.004 CHEN Guijun, ZHANG Xueying, LI Fenglian, et al. Risk prediction of water inrush from coal floor based on the εN-SVDD algorithm[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science), 2018, 37(1): 21−26. doi: 10.11956/j.issn.1008-0562.2018.01.004
[14] 曹庆奎,赵斐. 基于模糊−支持向量机的煤层底板突水危险性评价[J]. 煤炭学报,2011,36(4):633−637. CAO Qingkui, ZHAO Fei. Risk evaluation of water inrush from coal floor based on fuzzy-support vector machine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(4): 633−637.
[15] 杨志磊,孟祥瑞,王向前,等. 基于GA-BP网络模型的煤矿底板突水非线性预测评价[J]. 煤矿安全,2013,44(2):36−39. YANG Zhilei, MENG Xiangrui, WANG Xiangqian, et al. Nonlinear prediction and evaluation of coal mine floor water inrush based on GA-BP neural network model[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2013, 44(2): 36−39.
[16] 尹会永,周鑫龙,郎宁,等. 基于SSA优化的GA-BP神经网络煤层底板突水预测模型与应用[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(6):175−185. YIN Huiyong, ZHOU Xinlong, LANG Ning, et al. Prediction model of water inrush from coal floor based on GA-BP neural network optimized by SSA and its application[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(6): 175−185.
[17] 赵玲,陈磊琛,余小陆,等. SVM-KNN分类算法研究[J]. 计算机与数字工程,2010,38(6):29−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2010.06.009 ZHAO Ling, CHEN Leichen, YU Xiaolu, et al. Study on SVM-KNN classification algorithm[J]. Computer & Digital Engineering, 2010, 38(6): 29−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2010.06.009
[18] 阎馨,吴书文,屠乃威,等. 基于逻辑回归和增强学习的煤与瓦斯突出预测[J]. 控制工程,2021,28(10):1983−1988. YAN Xin, WU Shuwen, TU Naiwei, et al. Prediction of coal and gas outburst based on logistic regression and reinforcement learning[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2021, 28(10): 1983−1988.
[19] 张凌凡,陈忠辉,周天白,等. 基于梯度提升决策树的露天矿边坡多源信息融合与稳定性预测[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(S1):173−180. ZHANG Lingfan, CHEN Zhonghui, ZHOU Tianbai, et al. Multi-source information fusion and stability prediction of slope based on gradient boosting decision tree[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(S1): 173−180.
[20] 魏大勇. 优化疏降方案在刘桥二矿工作面水害防治中的应用[J]. 华北科技学院学报,2006,3(2):5−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7169.2006.02.002 WEI Dayong. Application of the optimum discharge procedure to groundwater hazard control in the work face in Liuqiao coal mine[J]. Journal of North China Institute of Science and Technology, 2006, 3(2): 5−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7169.2006.02.002



 下载:
下载: