Study on bearing characteristics and instability law of coal pillar dams under the effect of mining and water immersion
-
摘要:
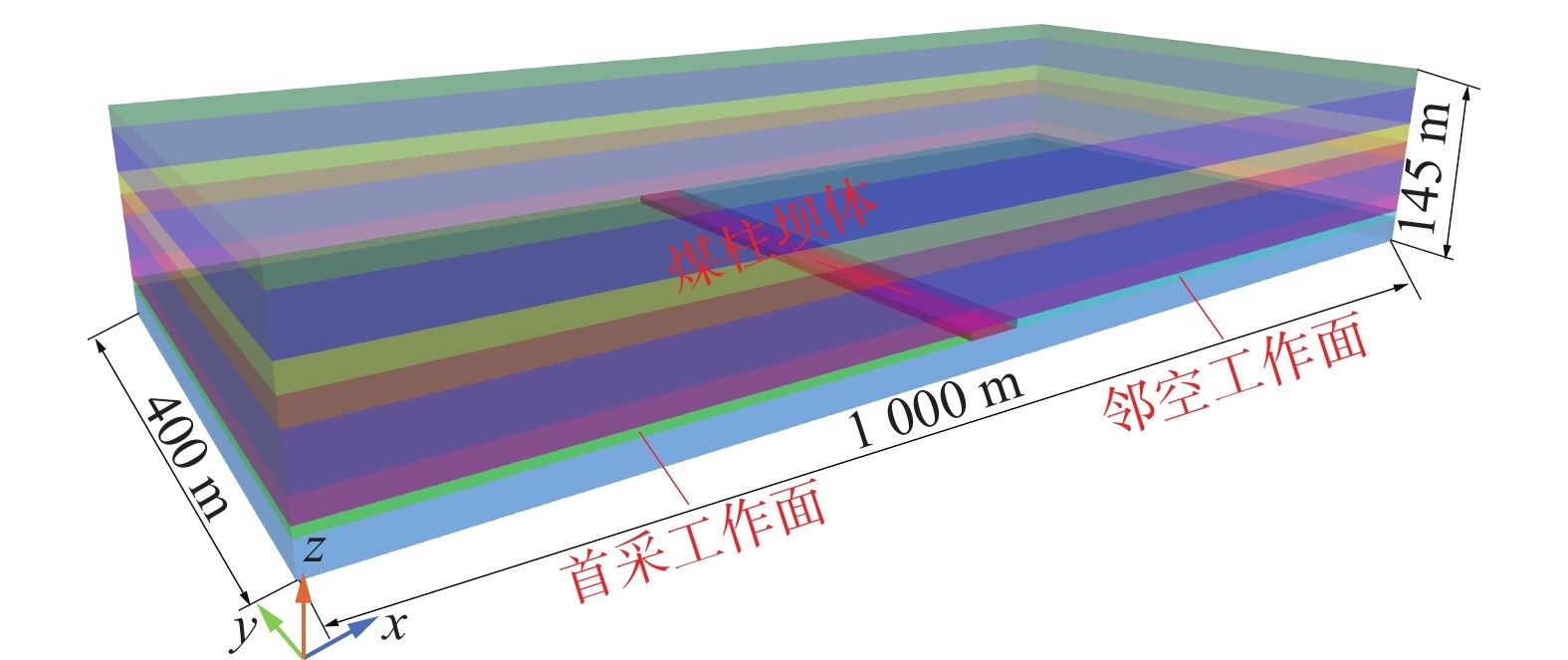
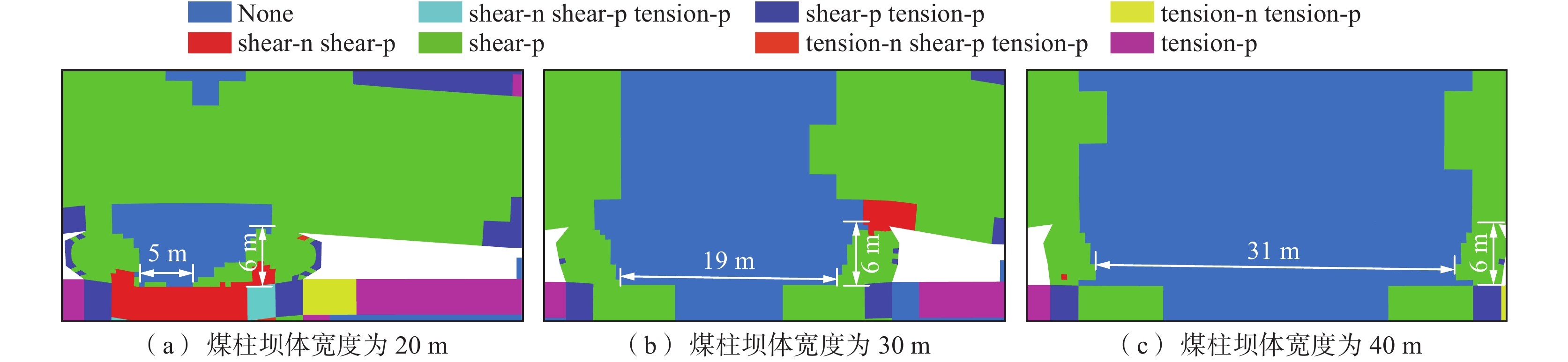
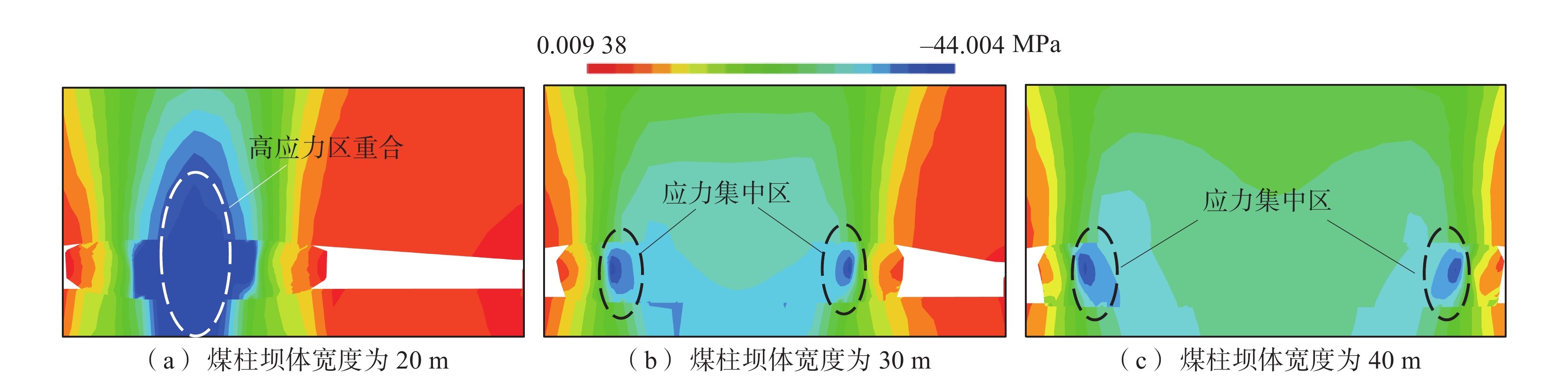
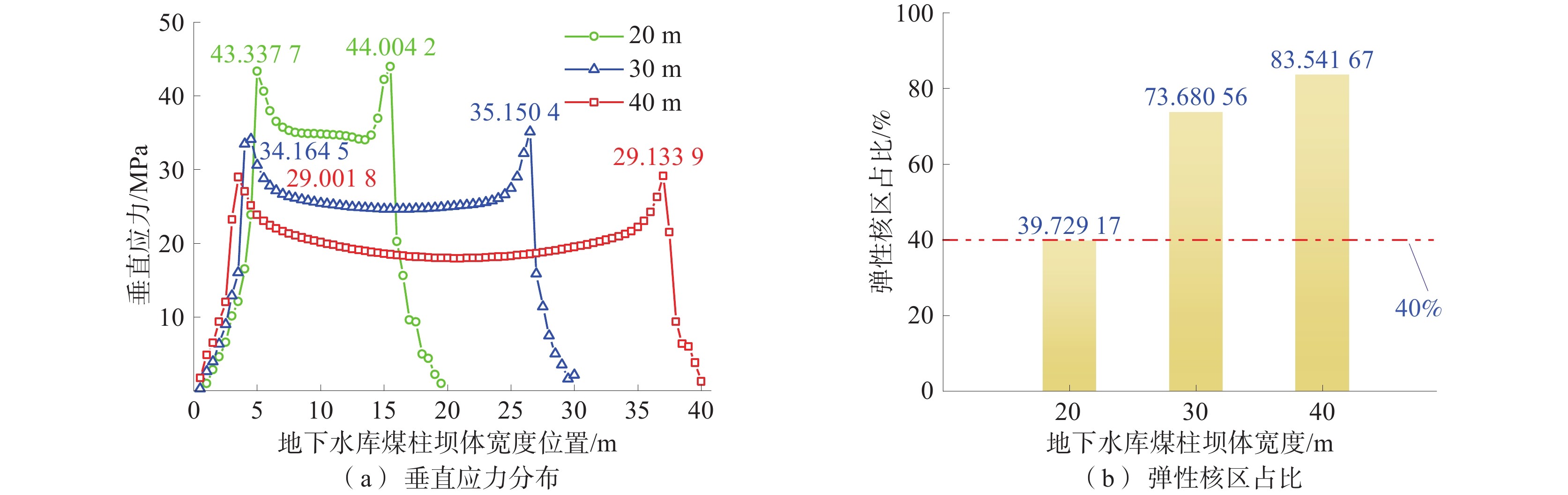
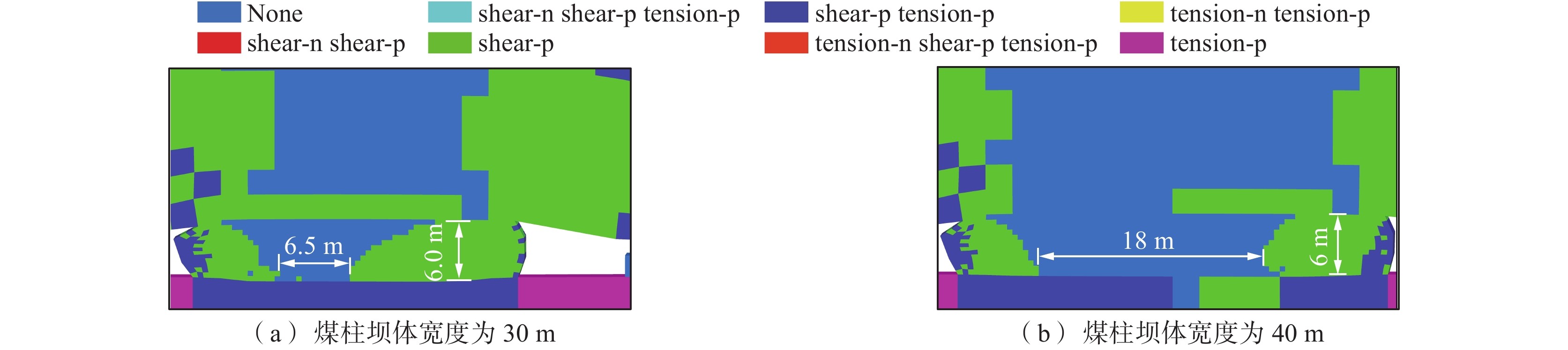
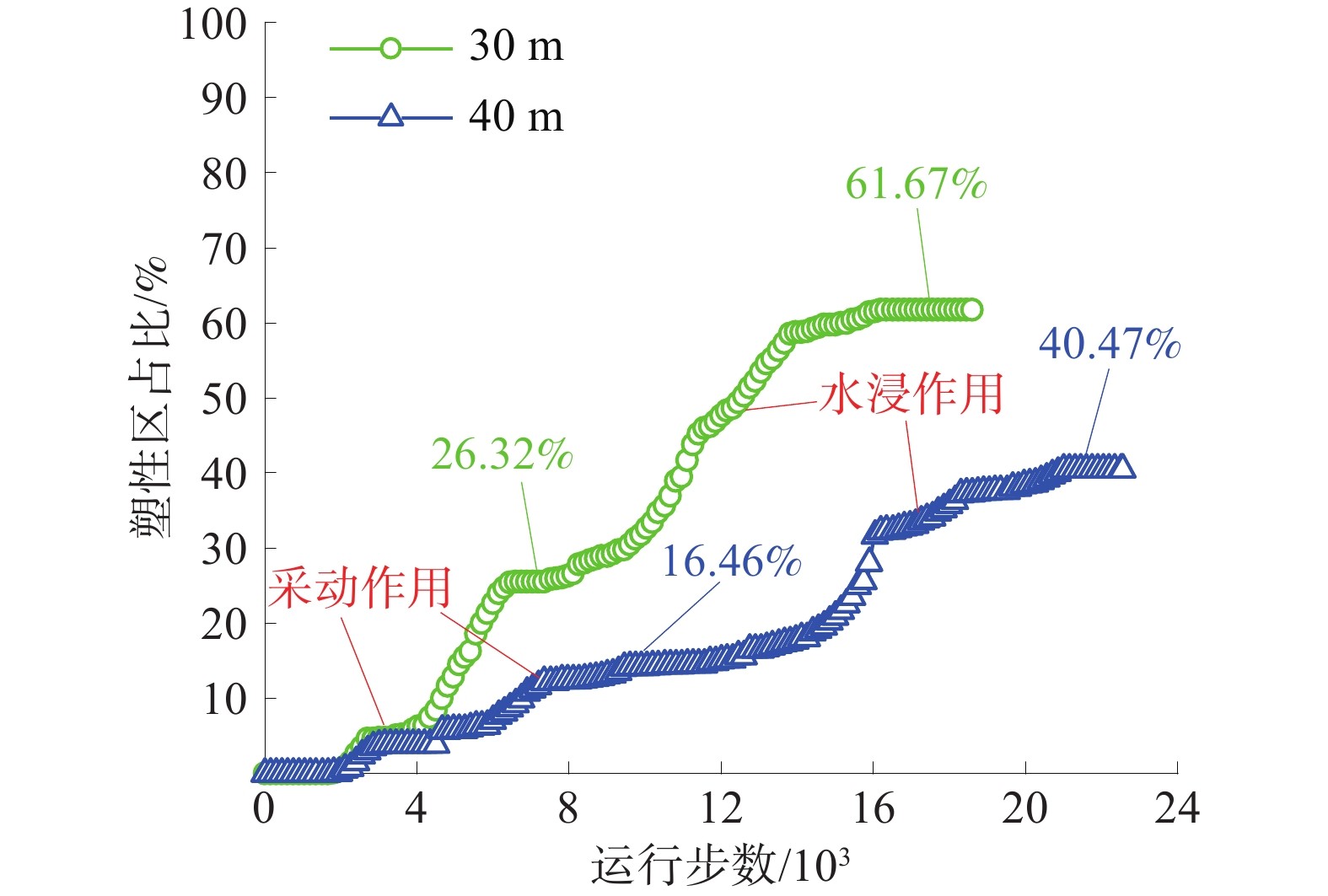
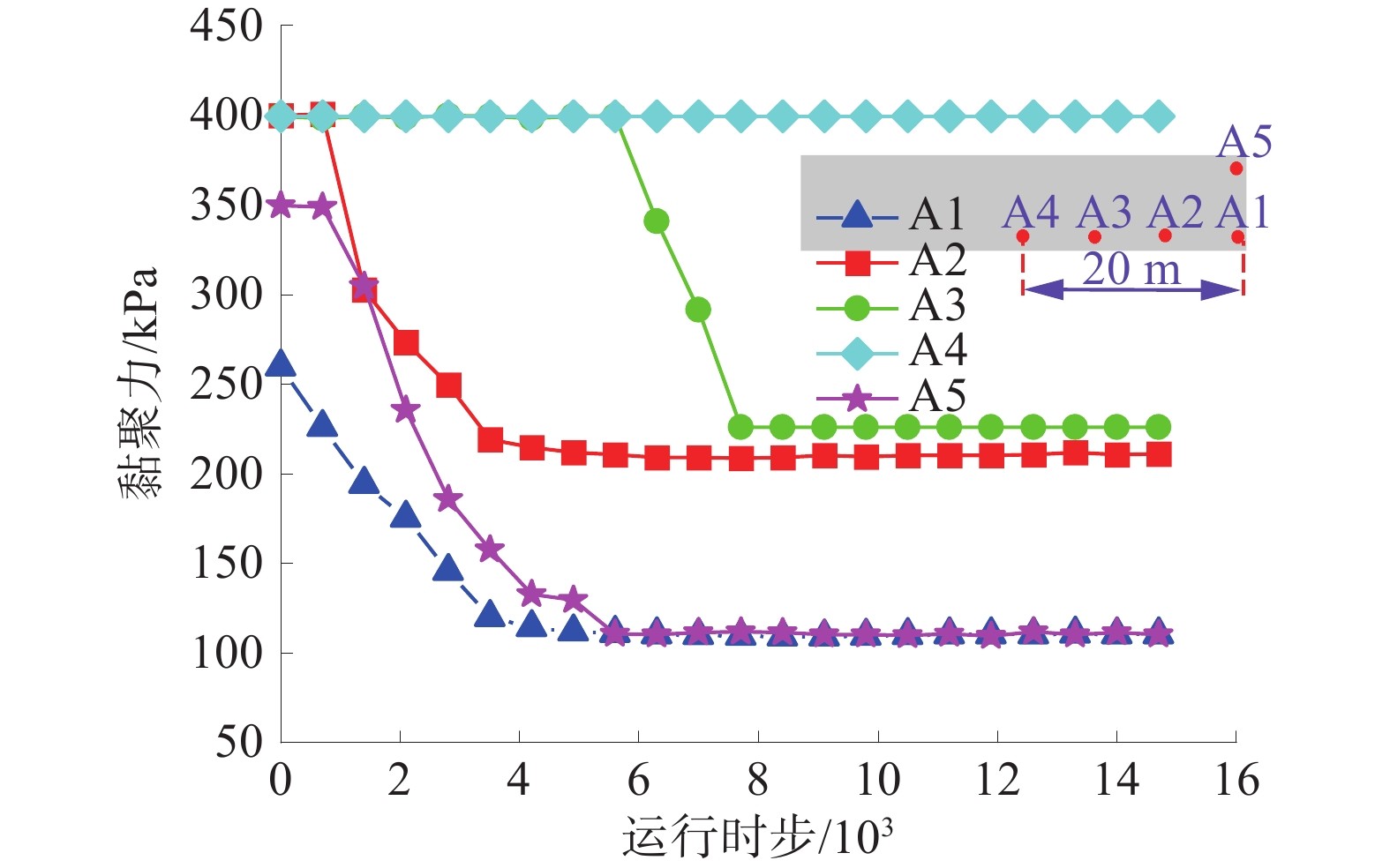
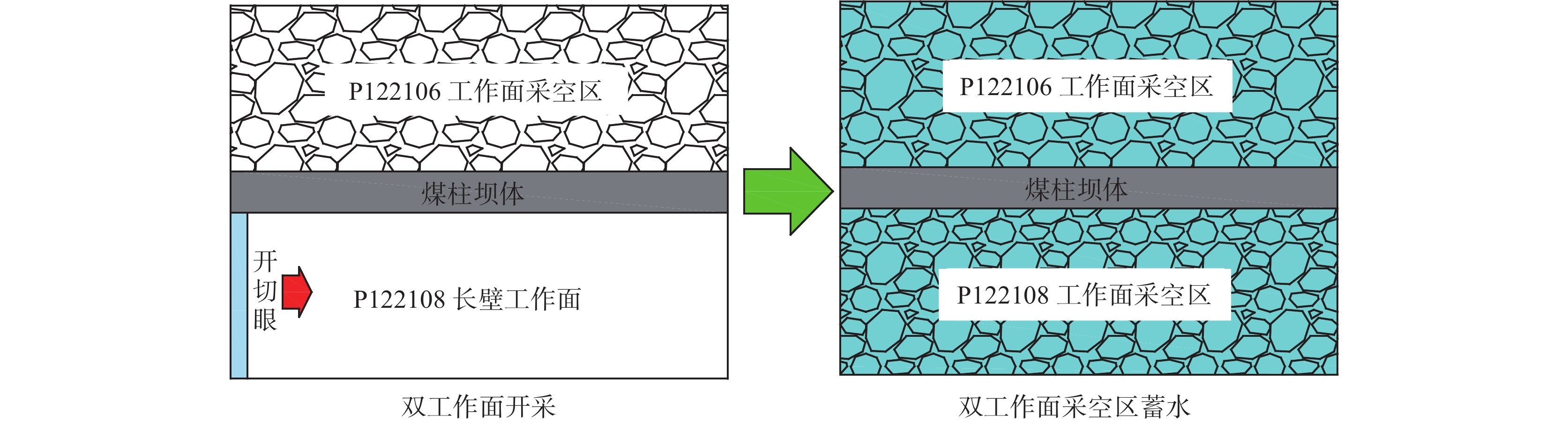
煤矿地下水库的储水技术已成为我国西部矿区煤炭资源开采与水资源保护协调发展的重要途径之一,而煤柱坝体的稳定性是煤矿地下水库能够安全并长期使用的关键因素。为了探究煤矿地下水库煤柱坝体在复杂条件下失稳特征,基于FLAC3D数值模拟及二次开发,以陕西北部某矿相邻工作面开采及采空区蓄水的水浸作用对煤柱坝体应力演化特征及稳定性的影响展开研究。结果表明:工作面开采完毕后,煤柱坝体应力分布均呈现双峰形,并随煤柱宽度的增加峰值逐渐下降,同时煤柱宽度为20 m时其弹性核区占比小于40%的临界失稳指标,将发生失稳;在采空区蓄水后,水浸作用下煤柱坝体塑性区占比增量呈现“稳定-增大-减小-稳定”的变化规律,能够很好地模拟水浸作用下煤柱坝体的“渗流-弱化-损伤-渗流”的渐进破坏特征;煤柱坝体的应力分布逐渐演化为拱形分布并趋于平均化,应力峰值大幅降低,同时,内部塑性区进一步扩展,弹性核区占比降低,且煤柱宽度的越小降低幅度越大;当煤柱宽度为30 m时,弹性核区占比降低为38.33%,将发生失稳;当煤柱留设宽度为40 m时,煤柱能够保持稳定。
Abstract:Coal mine underground reservoir water storage technology has become one of the important ways for the coordinated development of coal resource mining and water resource protection in western mining areas of China, and the stability of coal pillar dam body is one of the key factors for coal mine underground reservoir to be able to be used safely and for a long time. To investigate the destabilization characteristics of coal pillar dams in underground coal mine reservoirs under complex conditions, this paper is based on FLAC3D numerical simulation and secondary development to investigate the influence on the stress evolution characteristics and stability of coal pillar dams under the sequential action of adjacent workings mining and water flooding in the mining area in a mine in northern Shaanxi Province. The results show that the stress distribution of the coal pillar dam body shows a bimodal shape after the mining of the working face is completed. The peak value gradually decreases with the increase of the width of the coal pillar. At the same time, the elastic core area accounts for less than 40% of the critical instability index when the width of the coal pillar is 20 m, and instability will occur. After water storage in the mining area, the increment of the plastic zone of the coal pillar dam body under flooding shows the change law of “stable-increasing-decreasing-stable”, which can well simulate the progressive damage characteristics of “seepage-weakening-damage-seepage” of the coal pillar dam body under flooding. The stress distribution of the coal pillar dam body gradually evolves into an arch-shaped distribution. It tends to average out, and the peak stress is greatly reduced, while the internal plastic zone is further expanded and the percentage of its elastic core zone is reduced. The smaller the width of the coal pillar is, the greater the reduction is.
-
表 1 数值模拟中材料参数取值
Table 1 Values of material parameters in numerical simulation
岩性 密度/
(kg·m−3)体积模量/
GPa剪切模量/
GPa内摩擦角/
(°)黏聚力/
MPa抗拉强度/
MPa渗透系数/
(nm·s−1)孔隙率 中粒砂岩 2 500 11.61 9.09 28 1.00 2.30 0.060 0.45 砂质泥岩 2 400 2.57 1.45 26 0.55 0.80 0.006 0.35 粉砂岩 2 500 9.63 8.09 30 2.50 0.84 50.000 0.40 泥岩 2 141 2.21 1.24 24 0.52 0.83 65.000 0.40 细粒砂岩 2 400 2.13 0.93 26 0.45 0.35 0.006 0.30 煤层 1 400 2.13 0.93 25 0.40 0.25 80.000 0.50 -
[1] 黄庆享. 浅埋煤层保水开采岩层控制研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(1):50−55. HUANG Qingxiang. Research on roof control of water conservation mining in shallow seam[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(1): 50−55.
[2] 彭苏萍,毕银丽. 黄河流域煤矿区生态环境修复关键技术与战略思考[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(4):1211−1221. PENG Suping, BI Yinli. Strategic consideration and core technology about environmental ecological restoration in coal mine areas in the Yellow River basin of China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(4): 1211−1221.
[3] 顾大钊. 煤矿地下水库理论框架和技术体系[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(2):239−246. GU Dazhao. Theory framework and technological system of coal mine underground reservoir[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(2): 239−246.
[4] 顾大钊,李井峰,曹志国,等. 我国煤矿矿井水保护利用发展战略与工程科技[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(10):3079−3089. GU Dazhao, LI Jingfeng, CAO Zhiguo, et al. Technology and engineering development strategy of water protection and utilization of coal mine in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(10): 3079−3089.
[5] 顾大钊,颜永国,张勇,等. 煤矿地下水库煤柱动力响应与稳定性分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(7):1589−1597. GU Dazhao, YAN Yongguo, ZHANG Yong, et al. Experimental study and numerical simulation for dynamic response of coal pillars in coal mine underground reservoir[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(7): 1589−1597.
[6] 姚强岭,郝琪,陈翔宇,等. 煤矿地下水库煤柱坝体宽度设计[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(3):891−898. YAO Qiangling, HAO Qi, CHEN Xiangyu, et al. Design on the width of coal pillar dam in coal mine groundwater reservoir[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(3): 891−898.
[7] 姚强岭,刘亚鹏,陈田,等. 地下水库人工坝体强度损伤演化特征试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(4):1111−1117. YAO Qiangling, LIU Yapeng, CHEN Tian, et al. Experimental study of damage evolution of artificial dam strength of underground reservoir[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(4): 1111−1117.
[8] 张村,韩鹏华,王方田,等. 采动水浸作用下矿井地下水库残留煤柱稳定性[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2021,50(2):220−227. ZHANG Cun, HAN Penghua, WANG Fangtian, et al. The stability of residual coal pillar in underground reservoir with the effect of mining and water immersion[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2021, 50(2): 220−227.
[9] HAN P H, ZHANG C, WANG W. Failure analysis of coal pillars and gateroads in longwall faces under the mining-water invasion coupling effect[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2022, 131(1): 105912.
[10] 师维刚,张嘉凡,张慧梅,等. 防水隔离煤柱结构分区及合理宽度确定[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2017,36(5):1227−1237. SHI Weigang, ZHANG Jiafan, ZHANG Huimei, et al. Structural division and determination of rational width for waterproof partition coal pillar[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanicsand Engineering, 2017, 36(5): 1227−1237.
[11] 白东尧,鞠金峰,许家林,等. 李家壕煤矿地下水库人工坝体稳定性研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(7):1839−1845. BAI Dongyao, JU Jinfeng, XU Jialin, et al. Stability analysis of mine underground reservoir artificial dam in Lijiahao mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(7): 1839−1845.
[12] 刘少伟,王伟,王强,等. 缓倾斜煤层沿含水采空区掘巷煤柱稳定性研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(6):78−87. LIU Shaowei, WANG Wei, WANG Qiang, et al. Study on stability of coal pillars of roadway excavated along gob with water in gently inclined coal seam[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(6): 78−87.
[13] 王文才,李雨萌. 矿井地下水库坝体衔接处稳定性研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2020,51(5):88−92. WANG Wencai, LI Yumeng. Study on stability of joints in mine groundwater reservoir dam[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(5): 88−92.
[14] 李刚,刘海振,杨庆贺,等. 带压开采煤层底板破坏特征与突水风险分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2022,32(5):68−76. LI Gang, LIU Haizhen, YANG Qinghe, et al. Analysis on failure characteristics of coal seam floors and water inrush risks in mining under pressure[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(5): 68−76.
[15] 刘祥龙,江东海. 侧向渗透-轴向承载下煤样破坏及水-力耦合作用机制[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(12):175−181. LIU Xianglong, JIANG Donghai. Mechanism of coal sample failure and water-force coupling under lateral permeation-axial load[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(12): 175−181.
[16] 刘晓飞,薛宗建,牛滕冲. 水浸煤体周期应力承载特征研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(8):179−185. LIU Xiaofei, XUE Zongjian, NIU Tengchong, Study on periodic stress bearing characteristics of water-immersed coal body[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(8): 179−185.
[17] 姚强岭,王伟男,李学华,等. 水-岩作用下含煤岩系力学特性和声发射特征研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2021,50(3):558−569. YAO Qiangling, WANG Weinan, LI Xuehua, et al. Study of mechanical properties and acoustic emission characteristics of coal measures under water-rock interaction[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2021, 50(3): 558−569.
[18] ZHU W B, CHEN L, ZHOU Z L, et al. Failure propagation of pillars and roof in a room and pillar mine induced by longwall mining in the lower seam[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2019, 52(4): 1193−1209. doi: 10.1007/s00603-018-1630-y



 下载:
下载: