Ramp winch locking system based on multi-channel image processing
-
摘要:
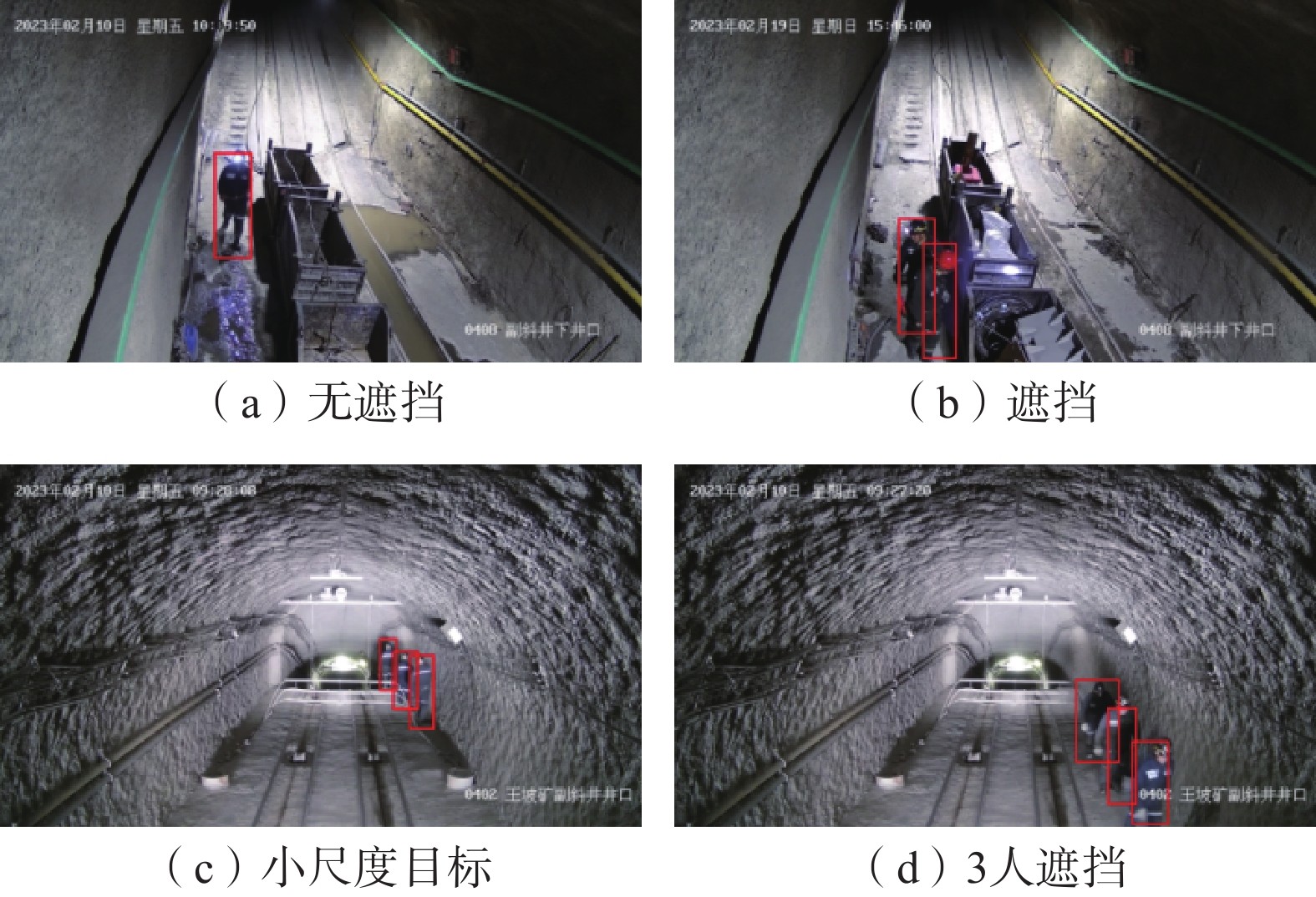
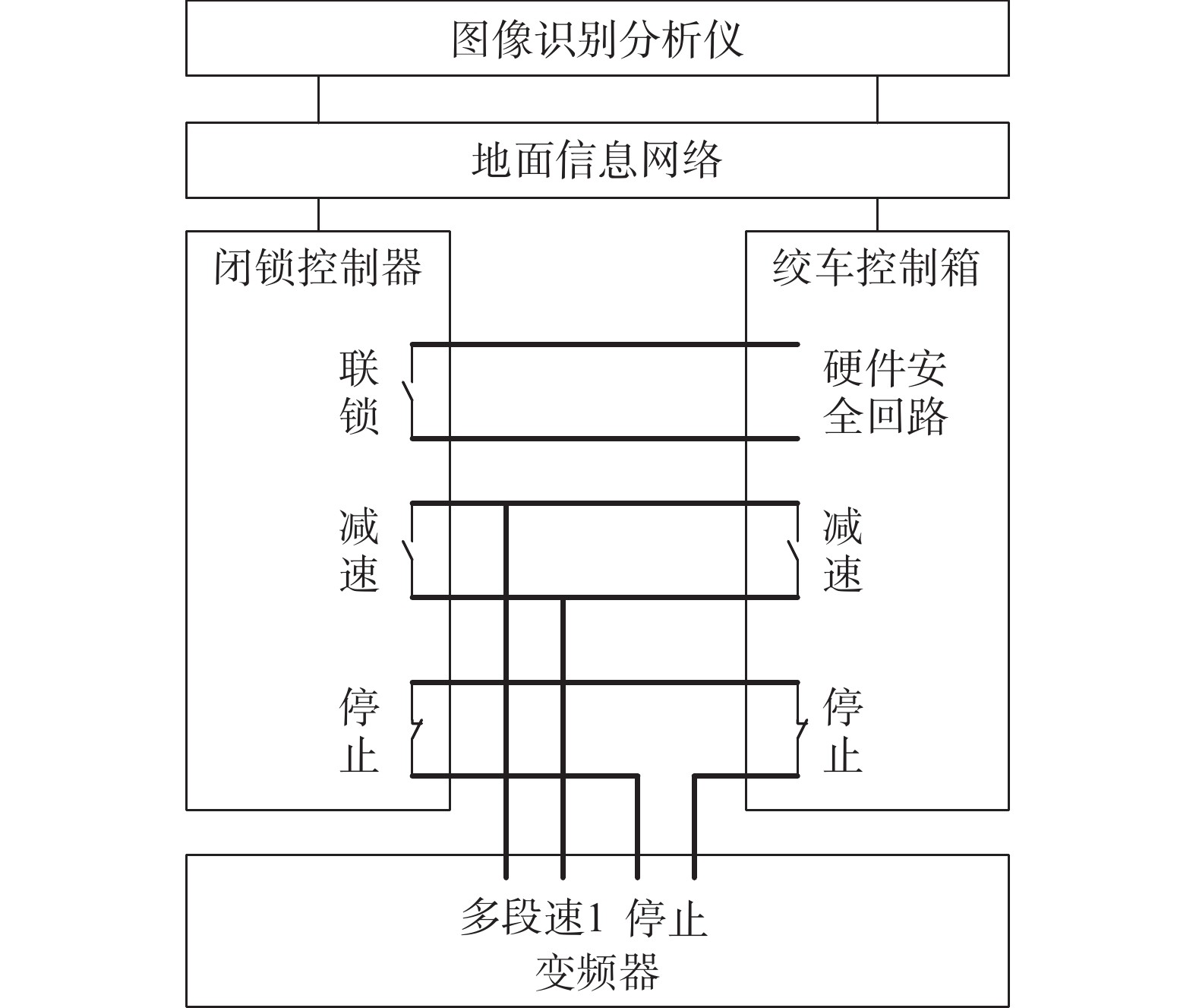
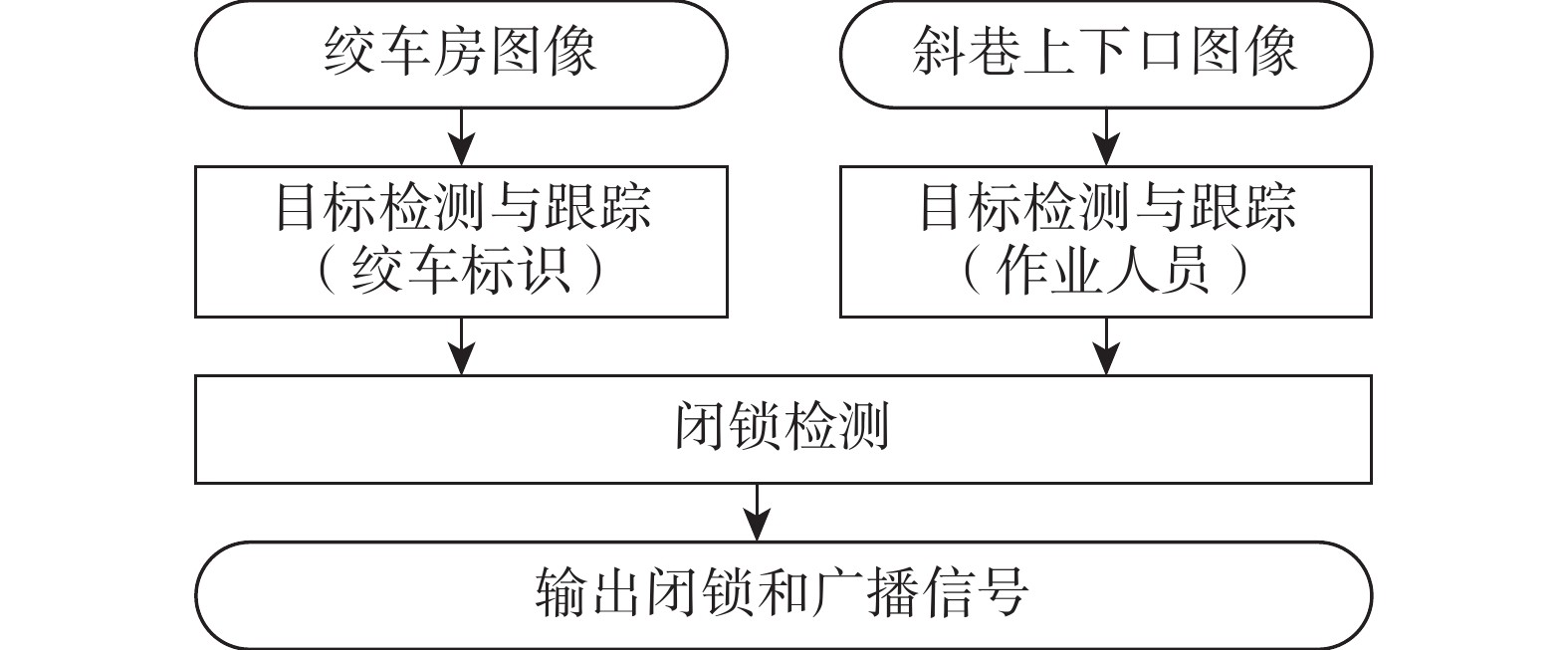
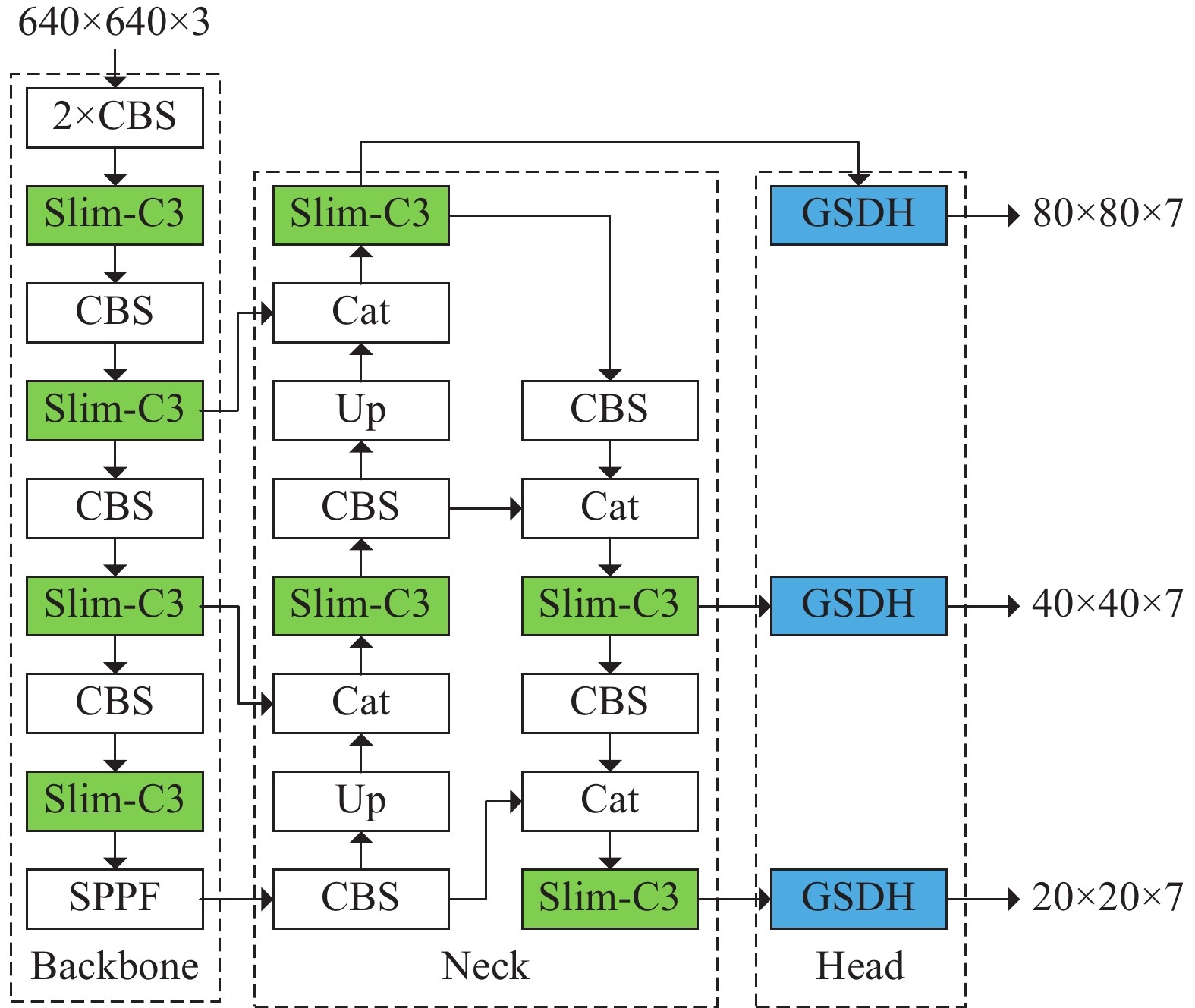
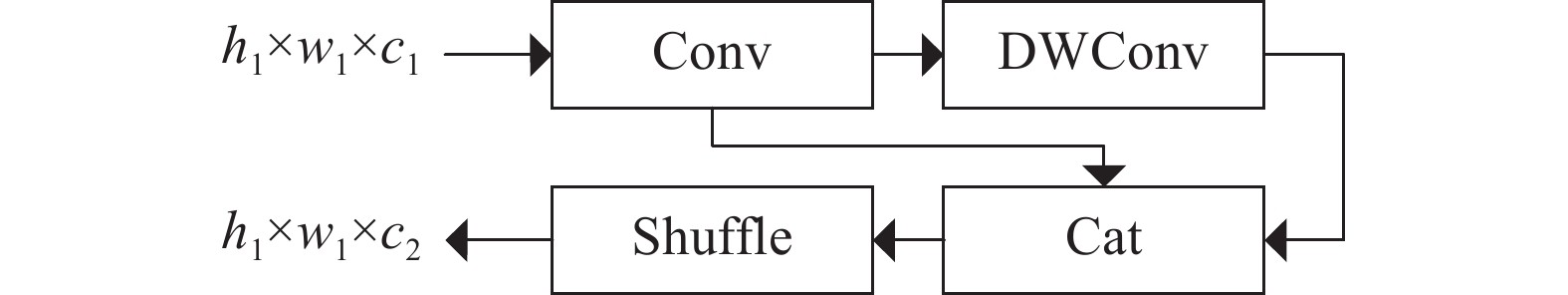
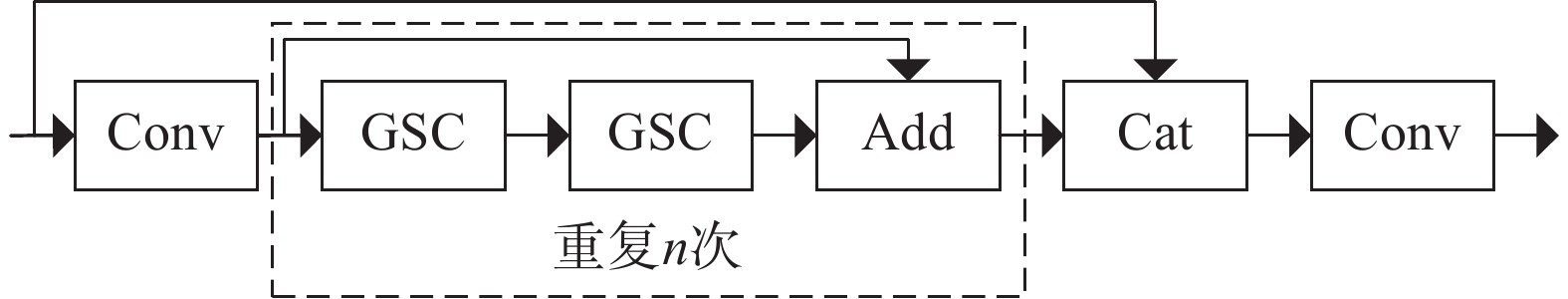
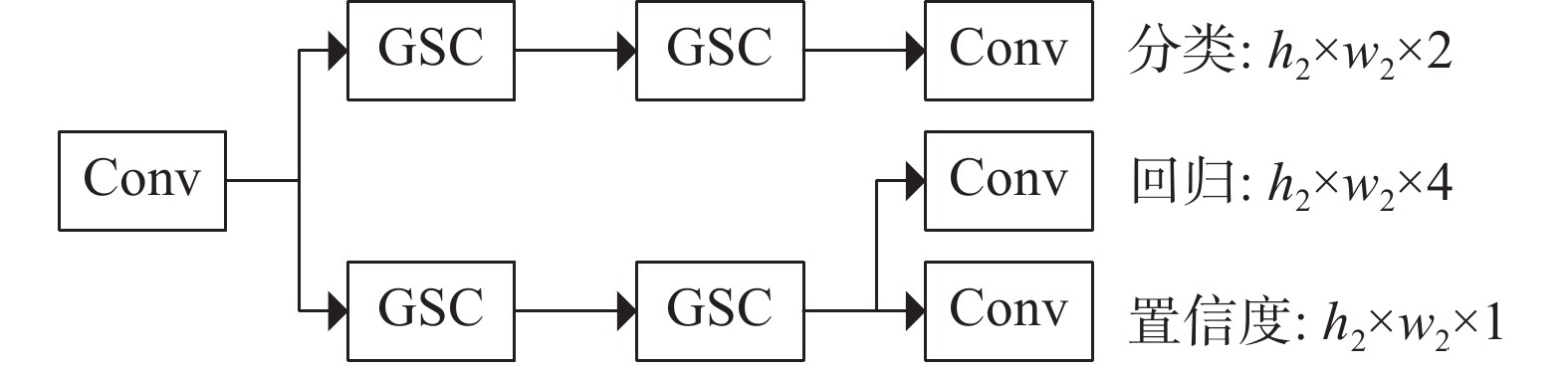
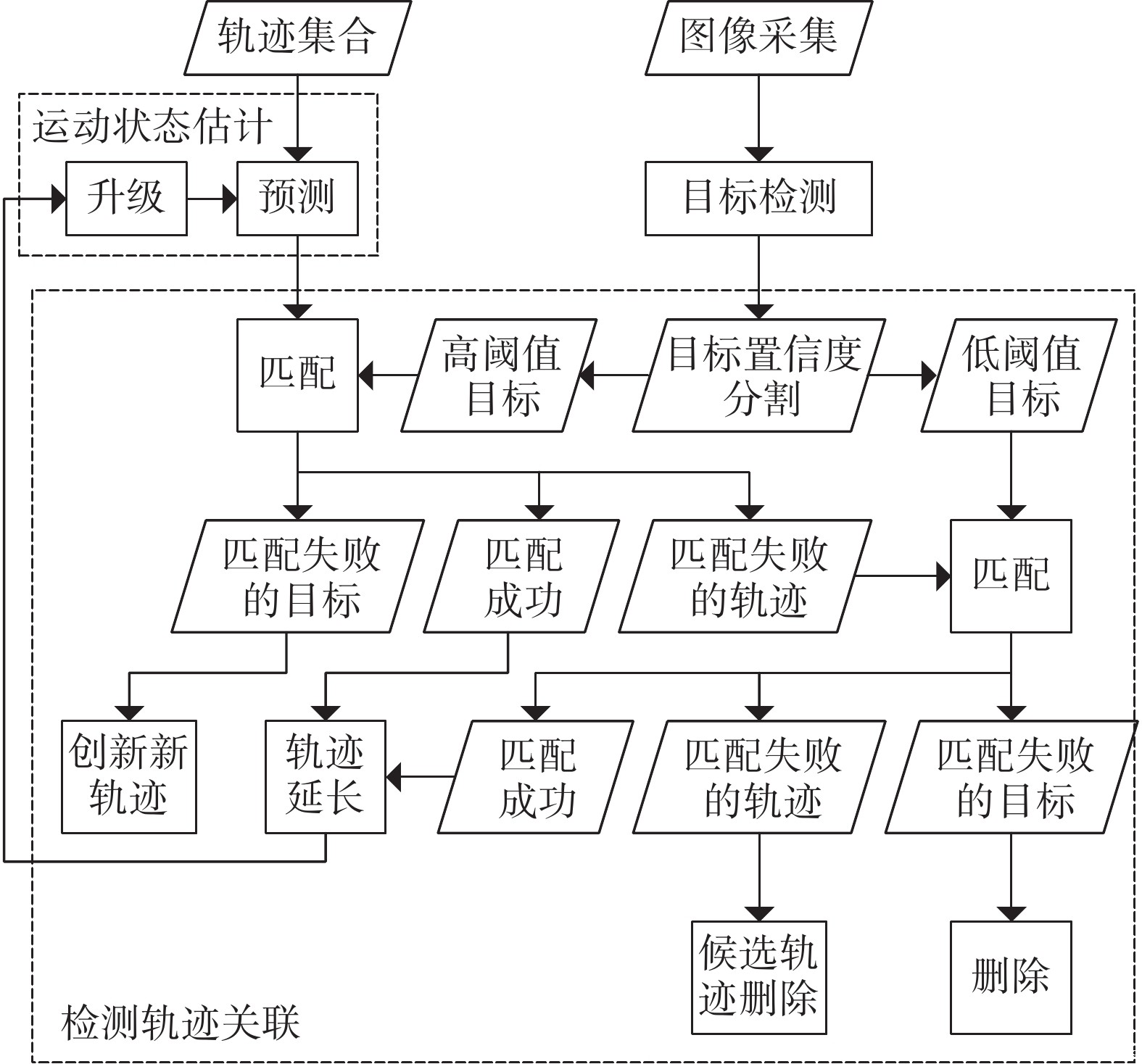
斜巷绞车运输闭锁系统是实现斜巷绞车运输“行车不行人”的重要手段。针对传统的闭锁系统存在准确度低、安装维护困难、硬件成本高的问题,研究了一种基于多通道图像处理的斜巷绞车运输闭锁检测算法,并研制了本安型闭锁检测系统。闭锁算法分为目标检测、跟踪以及闭锁检测。在目标检测阶段,利用GSConv设计了Slim-C3,对骨干和颈部网络进行轻量化处理,基于GSConv的解耦合头,提高目标检测精度;在目标跟踪阶段,研究了二级匹配的跟踪算法,在不降低检测精度的条件下,提升跟踪速度。试验表明:改进的目标检测模型的作业人员和绞车标识的AP0.5:0.95最优,比YOLOv8s分别提升了0.57%和1.65%;改进目标跟踪的IDF1比YOLOv8s+DeepSort提升了0.55%;改进的目标检测在人数统计的准确率和召回率分别为96.43%和93.10%。
Abstract:Ramp winch locking system is an important means of avoiding the simultaneous operation of winches and people walking in the ramp. The traditional locking system has the problems of low accuracy, difficult installation and maintenance, and high hardware cost, and for these problems, a ramp winch locking system based on multi-channel image processing is proposed, and an intrinsically safe locking dection system is developed. The algorithms are categorized into object detection, tracking and occlusion detection. In the object detection, Slim-C3 was designed using GSConv to lighten the backbone and neck networks and to improve the accuracy of target detection by the decoupling head based on GSConv; in the target tracking stage, the tracking algorithm of second-level matching is studied to improve the speed without decreasing the accuracy. The experimental results show that the proposed object detection optimized the AP0.5:0.95 for people and winch by 0.57% and 1.65% over YOLOv8s, respectively; the proposed tracking improved by 0.55% over YOLOv8s+DeepSort in IDF1; the precision and recall rates of the count were 96.43% and 93.10%, respectively.
-
表 1 目标检测模型性能对比
Table 1 Comparison of the performance of different object detections
模型 作业人员 绞车标识 Param/
106个FLOPs/
109次AP0.5/
%AP0.5:0.95/
%AP0.5/
%AP0.5:0.95/
%YOLOv3-tiny 69.81 42.29 77.54 43.29 8.72 10.67 YOLOv5s 73.07 51.01 89.05 55.04 7.12 8.35 YOLOv5s-GhostNet[14] 71.62 47.68 89.53 54.24 3.81 4.92 YOLOv7-tiny 72.91 49.87 87.97 55.77 6.08 8.24 YOLOv7-DGSTDGSM 70.23 44.32 88.36 54.17 2.98 4.33 YOLOv8s 78.17 55.40 93.02 60.34 12.76 15.50 YOLOv5s-GSC 76.82 55.97 92.73 61.99 5.85 7.59 表 2 消融试验结果
Table 2 Results of ablation test
Slim-
C3GS
Decoupled
Head作业人员 绞车标识 FPS
(INT8)/
(帧·s−1)FPS
(FLOAT32)/
(帧·s−1)AP0.5/
%AP0.5:0.95/
%AP0.5/
%AP0.5:0.95/
%有 无 69.15 41.33 82.96 50.67 226.77 51.89 无 有 77.10 54.48 91.52 62.01 157.91 33.53 有 有 76.82 55.97 92.73 61.99 193.43 45.84 表 3 目标跟踪性能对比
Table 3 Comparison of different target tracking performance
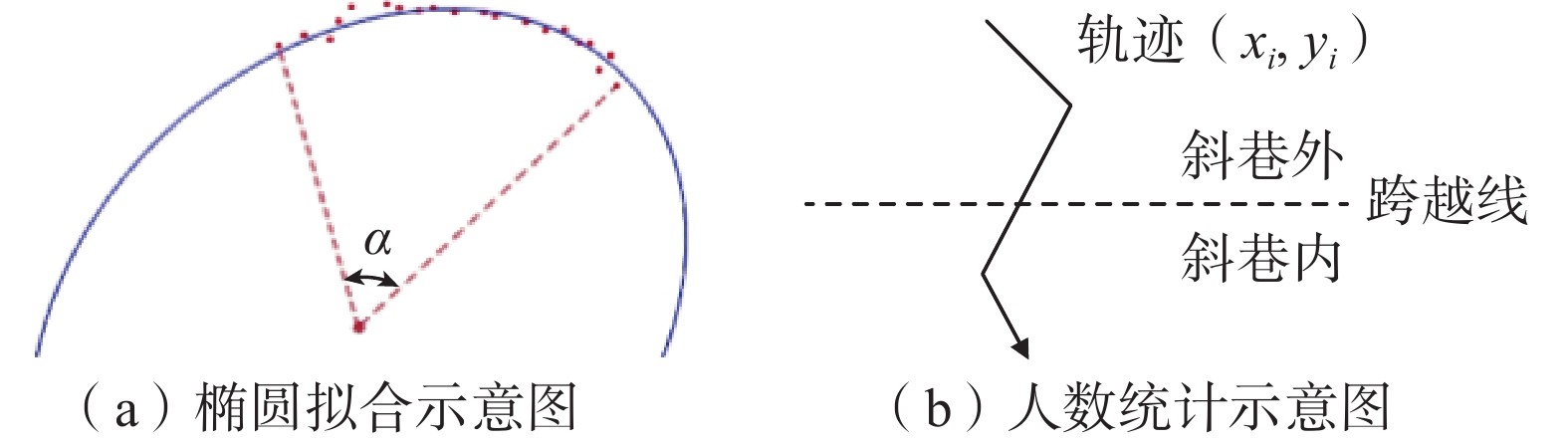
模型 MOTA/% IDF1/% FPS/(帧·s−1) TP/人 FP/人 FN/人 P/% R/% YOLOv8s+Sort[15] 71.94 66.54 77.05 274 22 45 92.57 85.89 YOLOv8s+DeepSort 78.02 73.92 30.69 291 16 28 94.79 91.22 YOLOv8s+BYTETrack 75.29 70.67 66.07 286 13 33 95.65 89.66 YOLOv8s+TLMTrack 76.96 72.76 68.68 294 10 25 96.71 92.16 YOLOv5s-GSC+Sort 72.55 68.41 112.80 277 26 42 91.42 86.83 YOLOv5s-GSC+DeepSort 77.02 72.44 35.12 295 14 24 95.47 92.48 YOLOv5s-GSC+BYTETrack 76.10 71.89 93.35 288 15 31 95.05 90.28 YOLOv5s-GSC+TLMTrack 77.33 74.47 95.72 297 11 22 96.43 93.10 注:MOTA(Multiple Object Tracking Accuracy, MOTA)为多目标跟踪精度;IDF1(Identification F1 score)为身份识别精度;TP为算法正确检测出越过跨越线的总人数;FP为没有人越过跨越线,但是算法检测出有人跨过检测线的总人数;FN为当视频中有人越过跨越线,但是算法没有检测出的总人数;P为$ \mathrm{准}\mathrm{确}\mathrm{率},P=\mathrm{T}\mathrm{P}/(\mathrm{T}\mathrm{P}+\mathrm{F}\mathrm{P}) $;R为召回率,$ R=\mathrm{T}\mathrm{P}/(\mathrm{T}\mathrm{P}+\mathrm{F}\mathrm{N}) $。 -
[1] 王虹,陈明军,张小峰. 我国煤矿快速掘进20年发展与展望[J]. 煤炭学报,2024,49(2):1199−1213. WANG Hong, CHEN Mingjun, ZHANG Xiaofeng. Twenty years development and prospect of rapid coal mine roadway excavation in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2024, 49(2): 1199−1213.
[2] 刘建荣,伊玉祥,徐杜民,等. 基于工业以太网的天祝煤矿斜巷多水平提升监控系统[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(5):166−169. LIU Jianrong, YI Yuxiang, XU Dumin, et al. Multi-level lifting monitoring system of inclined roadway in Tianzhu Coal Mine based on industrial Ethernet[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(5): 166−169.
[3] 李刚. 井下长距离遥控式设备列车组关键技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(5):203−207. LI Gang. Study on key technologies of long-distance remote-control train set in underground mine[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(5): 203−207.
[4] 吴畏,唐丽均,田国正. 矿用机车调度管理系统设计[J]. 工矿自动化,2018,44(7):17−21. WU Wei, TANG Lijun, TIAN Guozheng. Design of dispatching management system of mine-used locomotives[J]. Industry and Mine Automation, 2018, 44(7): 17−21.
[5] 李龙. 矿用斜巷轨道运输安全闭锁监控系统的研究[J]. 机械管理开发,2020,35(5):184−185. LI Long. Research on safety lockup monitoring system for mine slope lane transportation[J]. Mechanical Management and Development, 2020, 35(5): 184−185.
[6] 刘洋. 煤矿井下机车运输智能监控调度系统关键技术研究[J]. 能源与节能,2023(2):123−126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0802.2023.02.032 LIU Yang. Key technologies of intelligent monitoring and dispatching system for locomotive transportation in underground coal mines[J]. Energy And Energy Conservation, 2023(2): 123−126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0802.2023.02.032
[7] ZHAO Z Q, ZHENG P, XU S T, et al. Object detection with deep learning: A review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(11): 3212−3232. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2876865
[8] SEIDENSCHWARZ J, BRASO G, SERRANO V, et al. Simple cues lead to a strong multi-object tracker[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Vancouver, Canada, IEEE, 2023: 13813−13823.
[9] XU Y, BAN Y, DELORME G, et al. Trans Center: Transformer swith dense representations for multiple-object tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 45(6): 7820−7835.
[10] 徐彦威,李军,董元方,等. YOLO系列目标检测算法综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索,2024,18(9):2221−2238. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2402044 XU Yanwei, LI Jun, DONG Yuanfang, et al. Survey of development of YOLO object detection algorithms[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2024, 18(9): 2221−2238. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2402044
[11] 高小强,常侃,凌铭阳,等. 多模态自适应特征融合的目标检测[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2023,60(24):100−109. GAO Xiaoqiang, CHANG Kan, LING Mingyang, et al. Object detection via multimodal adaptive feature fusion[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(24): 100−109.
[12] ZHANG Y F, WANG C Y, WANG X G, et al. FairMOT: On the fairness of detection and re-identification in multiple object tracking[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(11): 3069−3087. doi: 10.1007/s11263-021-01513-4
[13] ZHANG Y F, SUN P Z, JIANG Y, et al. ByteTrack: Multi-object tracking by associating every detection box[C]// Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2022: 1−21.
[14] HAN K, WANG Y, TIAN Q, et al. GhostNet: more features from cheap operations[C]//2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 2020: 1577−1586.
[15] BEWLEY A, GE Z Y, OTT L, et al. Simple on line and real time tracking[C]//2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. IEEE, 2016: 3464−3468.



 下载:
下载: